Eczema is one of the most unpleasant skin conditions. When it happens parts of the skin will start to swell. There will be itching. Skin will turn reddish or pinkish in color. It will start with itching, after that, it will slowly progress into rashes, and the skin will start to dry off. Finally, the outer layer of the skin will start to peel off. For some people, this infection could reach a more advanced stage where the infected region will start to leak water like fluid. It will start to develop a shell-like structure on its top.
External Reasons
- Soap, detergents, shampoo, pesticides, nonage foods, some selective vegetables, and allergies towards certain fruits.
- Allergic towards cement, pollens, and pyrethrum.
- Infections from Staphylococcus bacteria, some types of virus, and yeast.
- Wearing ornaments made out of nickel or combination of nickel.
- Extreme weather conditions, both hot and cold.
- Being allergic or intolerant towards certain foods such as milk, egg, nuts etc…
- Depression or Stress
- Due to hormone changes that occur during periods and pregnancy in women.
- Allergies like atopic dermatitis. This mainly affects young children. Some parents are naturally overprotective of their kids. This can sometimes make their children immune deficient. Patients with atopic dermatitis are frequently affected by cough problems, dryness in eyes, and swelling, dryness in skin foldings.
Types of Eczema
Seborrheic dermatitis is a type of eczema. There is no identified precise reason for this condition yet. But, it is believed to be due to lack of immunity and certain nutrition deficiency.
Stasis Eczema is a condition found in people who are suffering from varicose veins. It is a skin condition that occurs when there is no proper blood circulation in the legs.
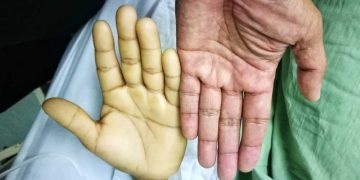
Hand Eczema happens to people who spend more time working with their hands in water. Additionally, it also occurs in people who spend more time with cement and detergents.
Three Stages of Eczema
There are three stages to Eczema that is classified based on its aggression.
- Acute Eczema
- Sub-acute Eczema
- Chronic Eczema
Acute eczema will have swelling, reddening of the skin and the affected region will release water like fluid. The affected skin surface will appear damp.
Chronic stage is when the skin condition lasts for years. It will be itchy, there will be rashes, swelling, affected region would have turned black, and the skin will become dry.
Sub-acute is a stage in-between acute and chronic. In this stage, the skin will shed off and outer surface will appear like a shell.

How to identity?
This problem can be found using patch test, and prick test. If the results of these tests are not conclusive then skin biopsy will be carried out to conclude the problem without any doubts.
What are the ways to prevent it?
- Using moisturizer regularly
- Preventing sweat or being without sweat as much as possible
- Reducing stress
- Reducing or avoiding the usage of woolen cloths
- Preventing of reducing the usage of soaps and detergents. It is always better to choose yellow colored detergent soaps over blue colored ones.
- Avoiding foods that you are allergic to
What are the treatments?
- Treatments will differ based on the severity of the condition.
- Initial treatments will involve reducing the reddishness and swelling of the skin surface.
- Ointments that contain steroids and antibiotic medicines will be prescribed if needed.
- If there are excess swelling and dryness, then the patient might be asked to use a moisturizer that contains salicylic acid. For some moisturizer that contains urea will be prescribed.
- Alternate ointments will be prescribed for people who are afraid of steroids.
- Some patients may need to consume medications to reduce itching.
- Mixing a packet of potassium permanganate in hot water, and soaking the foot in it will help a little to reduce the conditions of eczema.